Overindulging in ultra-processed foods can lead to stomach cancer: study
Admin
- 0

In a new study that adds more evidence to the connection between diet and health, researchers have discovered a link between the consumption of ultra-processed foods and an increased risk of developing cancers of the upper digestive tract, such as cancer of the mouth, throat and esophagus.
This research, funded by the International World Cancer Research Fund, reveals that those who consume 10% more ultra-processed foods have a significantly increased risk of head and neck cancer, as well as esophageal adenocarcinoma, a type of cancer that affects the glands inside the organs.
Dr Helen Croker, deputy director of research and policy at the International World Cancer Research Fund, highlights the importance of the study, saying it adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting a link between ultra-processed foods and the risk of cancer. However, she emphasizes the need for more research and data collection to fully understand the connection discovered in this report.
The study, published in the European Journal of Nutrition, analyzed diet and lifestyle data from 450,111 adult participants in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC).
Although the dietary data were collected in the 1990s, when consumption of ultra-processed foods was still relatively low, the results suggest that the association may be even stronger in cohorts with more recent assessments of dietary monitoring.
Contents
ToggleWhat ultra-processed foods does the study refer to?
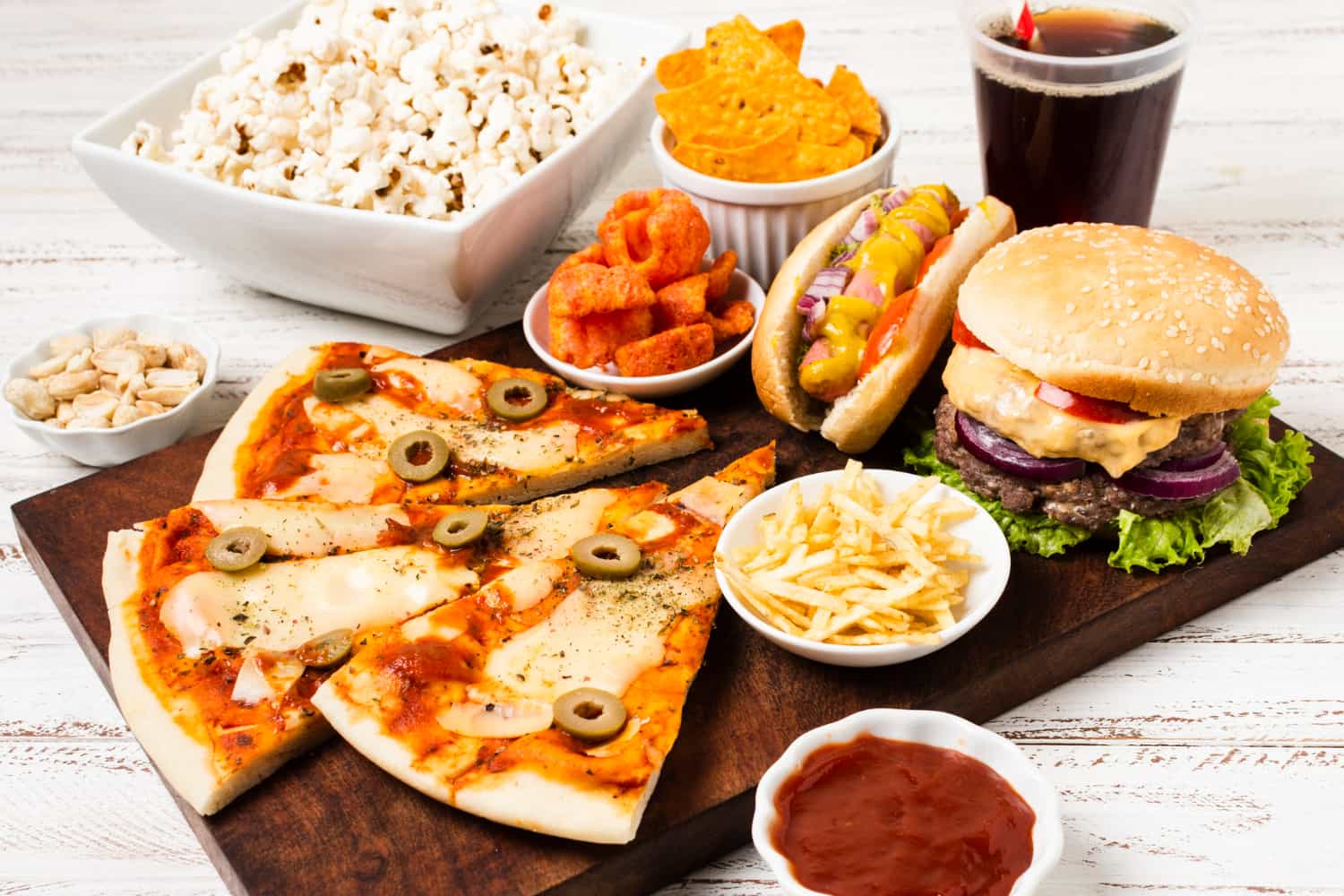
Ultra-processed foods such as soft drinks, chips, nuggets, packaged soups, ice cream, among others, contain ingredients and additives that are rarely used in home kitchens, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
These additives include preservatives, emulsifiers, artificial colors, antifoaming agents, thickeners and more, designed to improve the taste and appearance of final products.
The study also reveals a surprising finding: a connection between ultra-processed foods and accidental deaths. Although accidental death was used as a ‘negative control’ in the study, ultra-processed foods were associated with a higher rate of accidental death.
Also Read: US doctors are on alert due to an increase in flu cases
This raises intriguing questions about other factors related to ultra-processed foods, such as poverty, discrimination and environmental deterioration.
Although overweight and obesity are known risk factors for several types of cancer, statistical analysis of the results revealed that increased body fat explained only part of the association between ultra-processed foods and cancers. of the upper digestive tract.
This study suggests that other mechanisms, such as diet-induced inflammation, alterations in the microbiome, and adverse epigenetic effects, could be at play.
Dr. George Davey Smith, co-author of the study and professor of clinical epidemiology at the University of Bristol in the United Kingdom, highlights that although ultra-processed foods are clearly associated with adverse health outcomes, it is still unclear whether they are the direct cause. or whether underlying factors such as general health behaviors and socioeconomic position are responsible for the link.
This study adds to a series of research that has found associations between ultra-processed foods and various health problems, from cancer to heart disease and depression. As evidence continues to accumulate, attention is increasingly focused on the importance of a balanced, less processed diet for long-term health.